The Influences of Future of Work on Youth Labour Market Transitions in Nigeria
January 19by Lillian Efobi
The future of work is changing rapidly around the world and Nigeria is no exception. The country is undergoing a demographic revolution, with a young and growing population. This brings both opportunities and challenges to the youth labour market. On the one hand, the growing youth population represents a potential workforce that can stimulate economic growth. On the other hand, young people have difficulty finding stable jobs.
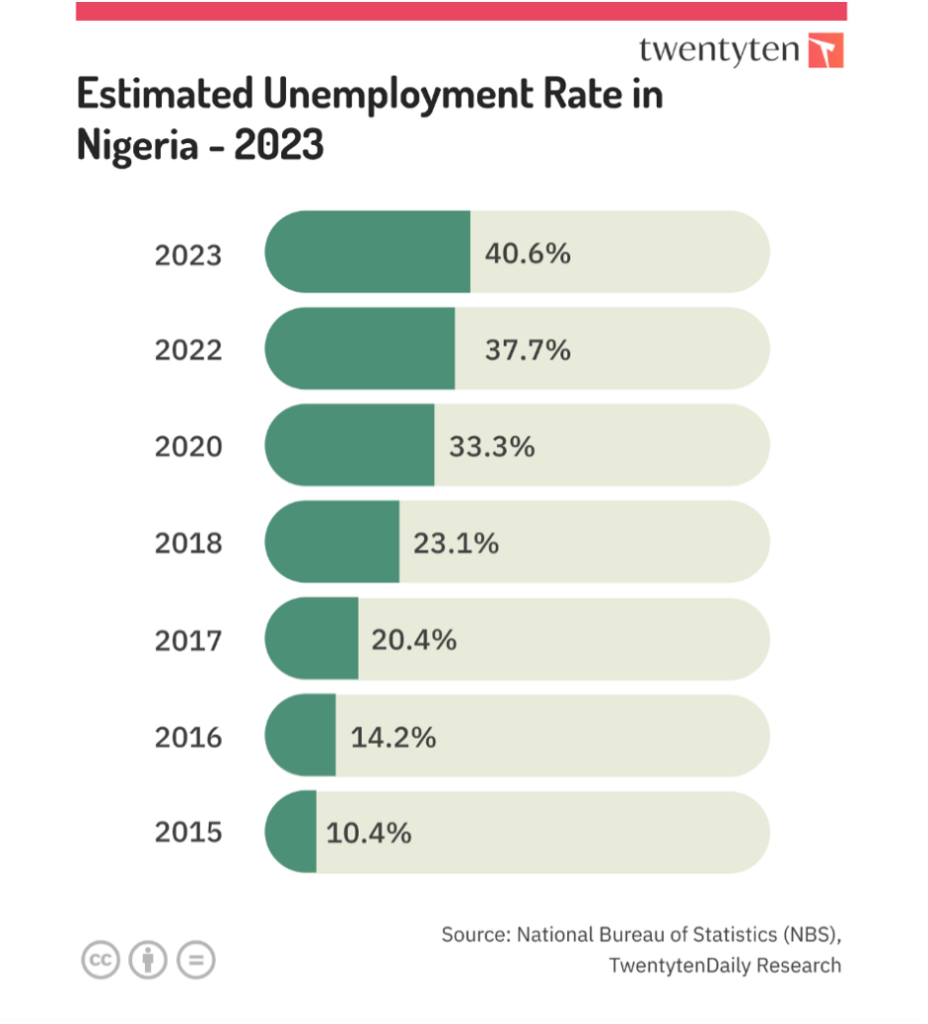
Youth unemployment in Nigeria is extremely high and a significant number of youths are engaged in informal and low-productivity jobs. The information technology (IT) revolution has had a significant impact on employment and the labour market. Some routine manual and cognitive tasks have been automated, replacing workers. In contrast, modern technologies complement and create new, non-routine social and cognitive tasks, making work in these tasks more efficient and creating new jobs. Recent applications of modern technology have improved the productivity of highly skilled workers, while they have had the opposite effect on middle-skilled workers. This has led to labour market polarization and increased economic inequality.
Solving the youth employment problem means finding solutions for young people looking for decent and productive work, for those who are working but living in poverty, or for those discouraged by market prospects. Those solutions must meet both labour supply through education, skills development, and training, and labour demand through job creation and a favourable environment for startups, as well as quality of work for young people including working standards and conditions.
The youth labour market situation in Nigeria is also affected by developments across national borders, such as population growth, climate change, migration, innovation, and automation, as well as calls for bold and urgent action by all stakeholders. More recently, the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and the measures introduced to contain it have put further pressure on the economy, the labour market, and the employment prospects of young people. Nigeria remains committed to ensuring sustainable and productive employment for its youth. Globally, Nigeria supports the implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and became the first government partner in Africa to commit to the Global Initiative for Decent Work for Youth.
Government policies such as the National Youth Policy and more, modern technology, globalization, increase in population growth are key Determinants of the future of employment in Nigeria. The question remains, what can the youth do to prepare themselves for the future of work, without waiting for the government?
The future of work influencing the transformation of the youth labour market in Nigeria can be through a growing demand for skills such as problem solving and critical thinking. Also, the future of work will promote flexibility of labour through remote work and freelancing with requisite skills to compensate. New jobs will emerge in sectors such as Agriculture, renewable energy, and information technology.
The Nigerian youth will however be faced with challenges such as: Mismatch between skills and labour market needs, Lack of access to education and training and Limited employment opportunities due to the high unemployment rate. What then can be done to address these challenges? The Nigerian government should invest in education and training to empower young people with skills for the future. Policy formulation and implementation that will favour the rise of entrepreneurs of the future should be promoted and both the private and public sector should create jobs for young people. To empower the Nigerian youth for the future of work, the collaboration should be at the centre between the government, private sector, and charities. Apprenticeships and internships should be provided for students from secondary to tertiary levels and technical skills should be encouraged at the primary education level. Access to business support, finance, training and mentoring for young entrepreneurs.